Accessories for enclosures
Accessories for enclosures
-
Products
Products Enclosures and tuning knobs
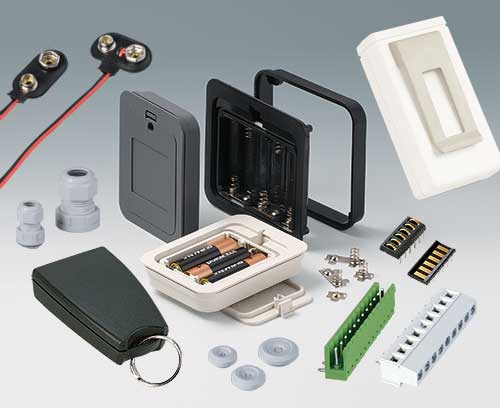
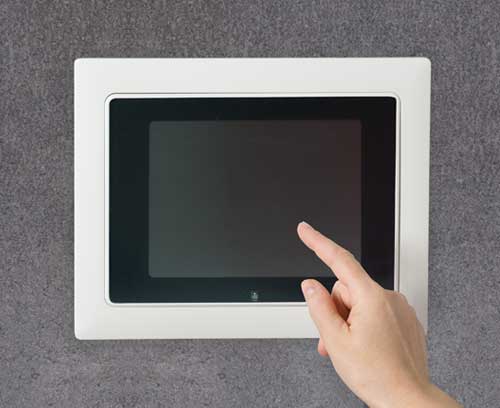
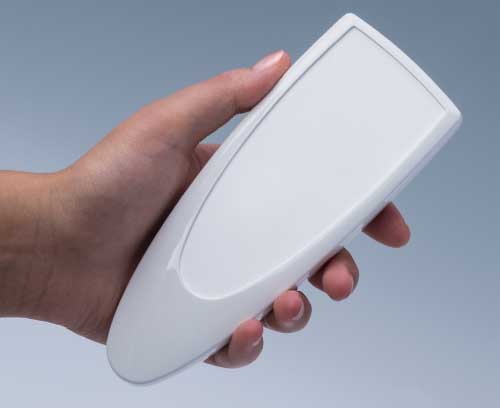
Modern plastic enclosures, aluminium enclosures and tuning knobs for many different applications: Handheld enclosures, wall-mount enclosures, table top enclosures, DIN rail enclosures etc. Take a look for yourself!
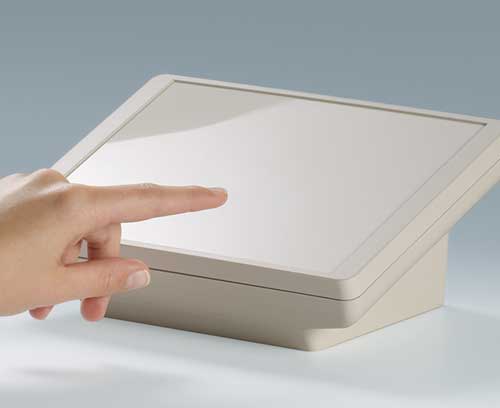
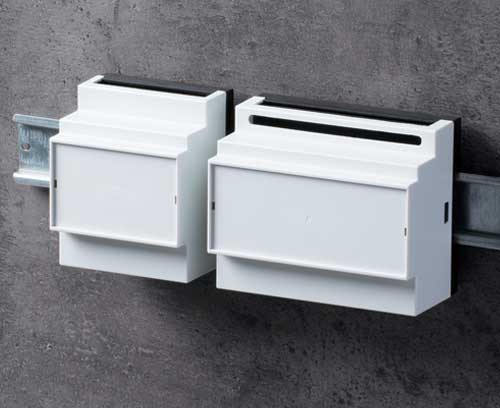
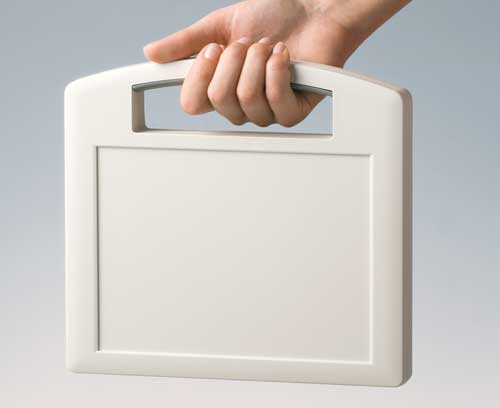
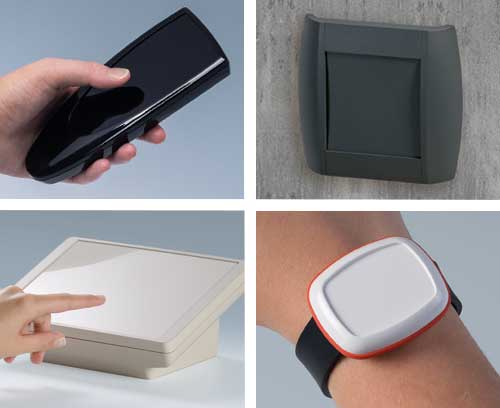
 Plastic enclosures Advanced plastic enclosures for electrical and electronics equipment
Plastic enclosures Advanced plastic enclosures for electrical and electronics equipmentFor up-to-date enclosure design. Gain an overview and choose from our wide range.
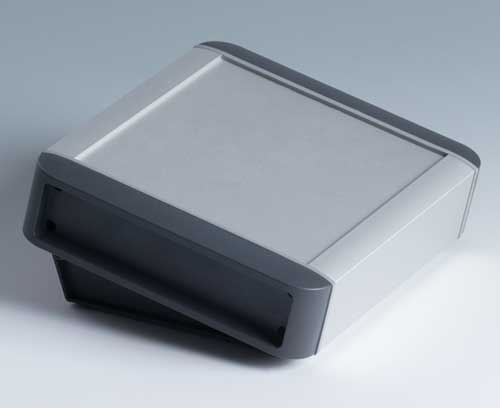
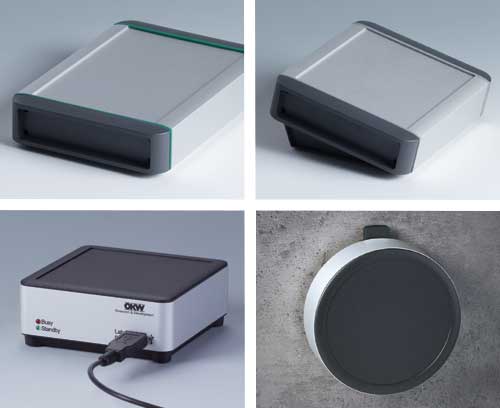
 Aluminium enclosures High quality aluminium profile enclosures with attractive plastic end panels
Aluminium enclosures High quality aluminium profile enclosures with attractive plastic end panelsStylish and robust protection for your electronics. Aluminium profiles available in special lengths on request.
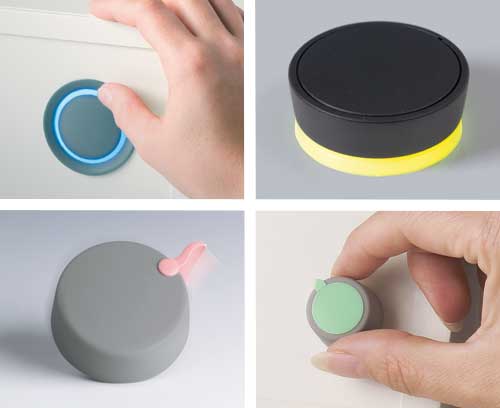
 Potentiometer / Tuning knobs Extensive range of tuning knobs: ergonomic, modern and classic designs
Potentiometer / Tuning knobs Extensive range of tuning knobs: ergonomic, modern and classic designsWell-proven for rotary potentiometers with round and flattened shaft ends according to DIN 41591 or 6/4.6 mm.

-
Customising
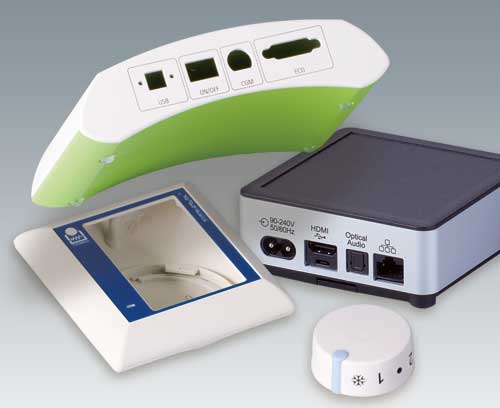
Customising We can supply the enclosures to your exact requirements, installation-ready
Tell us what you need to complete your particular product design. We can process and finish our enclosures and tuning knobs accordingly. Learn more about our services here…
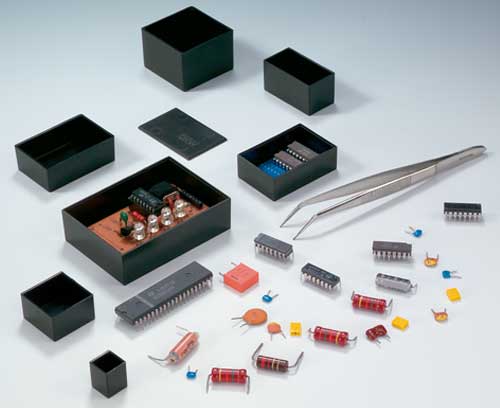
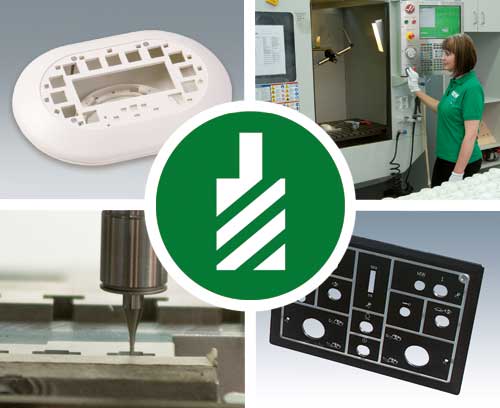
 Machining Fast, high quality and accurate machining to your specifications
Machining Fast, high quality and accurate machining to your specificationsCutouts / openings for interfaces, displays, operating elements, cable inlets and outlets, tapped holes, recesses for decoration foils etc.
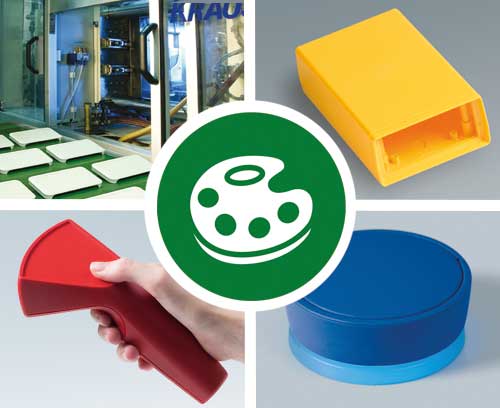
 Lacquering We can lacquer our products with highly attractive and tough finishes for demanding use
Lacquering We can lacquer our products with highly attractive and tough finishes for demanding useChoose your company colour or a protective lacquer for special requirements, e.g. ESD lacquer.
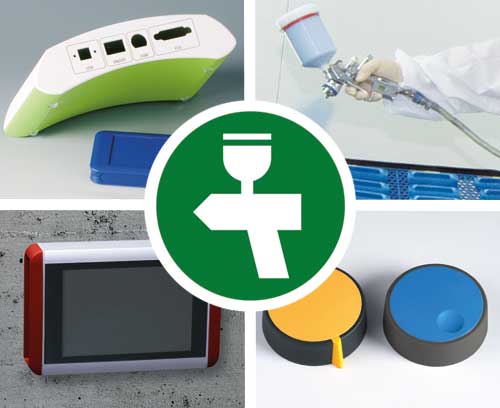 Printing We can print enclosures, front panels and tuning knobs using screen/tampo printing and digital printing
Printing We can print enclosures, front panels and tuning knobs using screen/tampo printing and digital printingLogo, text and graphics printed in your colours.
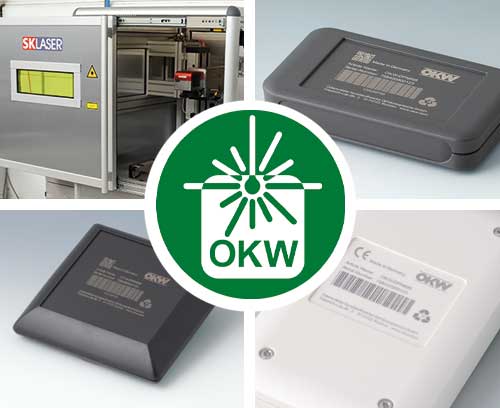
 Laser marking We offer laser marking for numerous enclosures and components from our standard range
Laser marking We offer laser marking for numerous enclosures and components from our standard rangeFor individual labelling, identifying or marking, e.g. logo, text, graphics, codes, numbering etc.
 Decor foils We can print decor foils digitally, in photo quality, for labelling the enclosures
Decor foils We can print decor foils digitally, in photo quality, for labelling the enclosuresFoils without/with embossing for key functions, display / LED windows, barcodes etc.
 Special material We can also mould our plastic enclosures and tuning knobs in special colours
Special material We can also mould our plastic enclosures and tuning knobs in special coloursYour individual colour matched to a sample, RAL, Pantone etc.
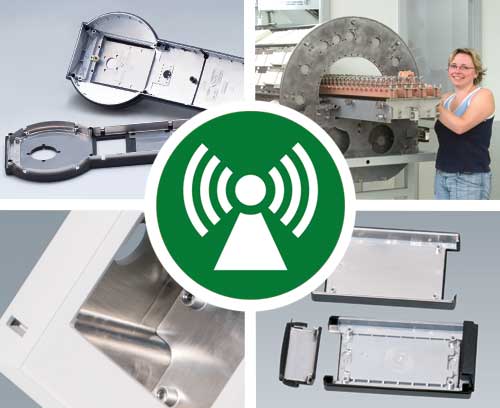
 EMC shielding Order your plastic enclosures coated with aluminium on the inside to protect against RFI/EMI
EMC shielding Order your plastic enclosures coated with aluminium on the inside to protect against RFI/EMISafe and reliable thanks to application-oriented shielding.
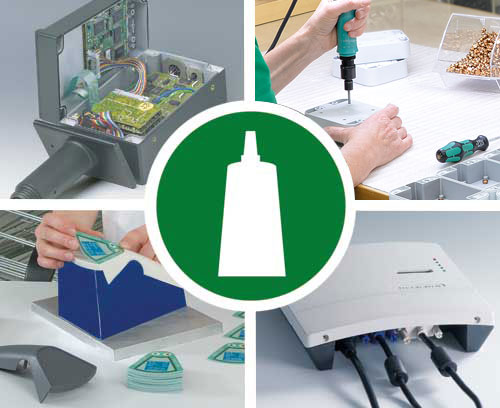
 Installation / Assembly of accessories We perform assembly work to complete the enclosure assembly or device
Installation / Assembly of accessories We perform assembly work to complete the enclosure assembly or deviceAssembly of enclosure accessories, bonding of decor foils and display screens, component assembly, individual installation with spacers, fastening pillars etc.
 Partner solutions We cooperate with expert partners
Partner solutions We cooperate with expert partnersThanks to partnerships for input systems and power supplies, we can offer you individually tailored enclosures as complete solutions.

-
Applications
Applications In-depth application know-how
Examples of customer applications show the variety of options for using our enclosures and tuning knobs. Choose the application for which you would like to obtain further information.
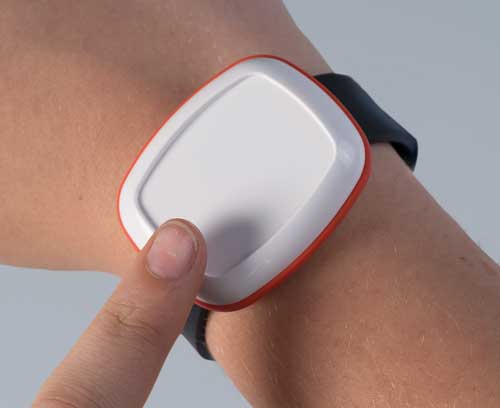
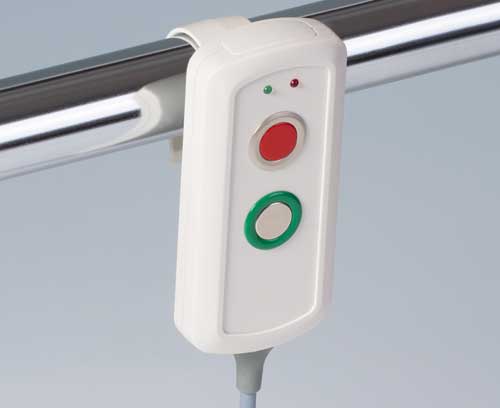
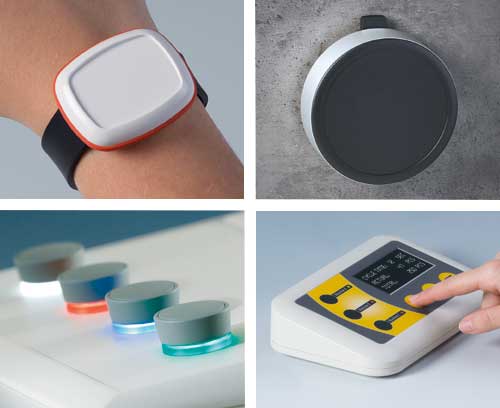
 Medicine / Laboratory / Wellness Man and ergonomics
Medicine / Laboratory / Wellness Man and ergonomicsOKW focuses on innovative and high-quality solutions with ergonomically favourable shapes that create trust.
 Measuring / Control / Automation Man and precision
Measuring / Control / Automation Man and precisionOKW solutions guarantee high operating comfort and safety in everyday use.
 Mechanical engineering / Plant building Man and production
Mechanical engineering / Plant building Man and productionOKW solutions are user-friendly and easy to read off, and are also characterised by reliability.
 Automotive engineering / Construction equipment / Military / Aviation Man and mobility
Automotive engineering / Construction equipment / Military / Aviation Man and mobilityWith their robust design and high-quality materials, OKW enclosures and tuning knobs can even withstand tough conditions.
 Heating / Climate / Environment Man and efficiency
Heating / Climate / Environment Man and efficiencyOKW develops solutions to meet your needs so that you and your users can enjoy the devices in the long run.
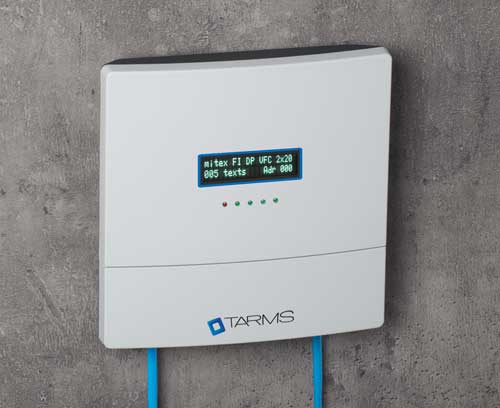
 Security / Building services systems Man and technology
Security / Building services systems Man and technologyOKW is a pioneer in the development of state-of-the-art solutions to achieve progress in smart technologies.
 Communication Man and information
Communication Man and informationOKW sets new standards so that you can get the most out of your information and communication processes.
 Mining / Gas / Oil Man and raw materials
Mining / Gas / Oil Man and raw materialsHarsh environments - OKW has solutions that provide a high quality standard for the protection of your electronics.

-
News
News
Full details about all our new products and services along with company news.
 News
NewsFull details about all our new products and services along with company news.
Press ReleasesRead our latest company press information and our complete press releases archive.
 Blog
BlogOur blogs cover industry trends, how to's, customer applications, FAQs, international product standards and details about our new products and services.

-
Technical Information
- Technical Information
- How To Request A Sample/Quotation
- How To Download 2D/3D Drawings
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Brochures, Assembly Instructions, Certifications
- Ordering Information
- How To Specify Enclosures
- A Guide to Enclosures Plastics
- IP Ratings Explained
- UL 94 Flammability Test
- Viewers/Plug-ins
TECHNICAL INFORMATIONMaterial selection, international standards, protection classes, flammability tests, environmental directives etc.
 HOW TO GET A SAMPLE OR QUOTE
HOW TO GET A SAMPLE OR QUOTEUse our basket facility to compare different enclosures and tuning knobs, create your own parts lists, and request samples and a quotation.
 HOW TO DOWNLOAD OKW DRAWINGS
HOW TO DOWNLOAD OKW DRAWINGSDownload our drawings in 2D (PDF, DWG, DXF) and 3D (x_t, step, sat) formats.
 FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS (FAQ) Frequently asked questions (FAQ) about plastic enclosures, aluminium enclosures and potentiometer tuning knobs for electronicsDOWNLOAD AREA
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS (FAQ) Frequently asked questions (FAQ) about plastic enclosures, aluminium enclosures and potentiometer tuning knobs for electronicsDOWNLOAD AREA- INSIDE company magazine
- Assembly instructions
- Publications
- Certifications such as our ISO 9001:2015. ORDERING INFORMATION
ORDERING INFORMATIONFull information on how to place an order along with payment and delivery details.
 YOUR GUIDE TO SPECIFYING ENCLOSURES
YOUR GUIDE TO SPECIFYING ENCLOSURESReduce project costs and save time – read this guide before you specify your enclosures...
 PLASTICS USED FOR OUR ENCLOSURES
PLASTICS USED FOR OUR ENCLOSURESThe most common plastics we use in the manufacture of our enclosures are detailed here.
 IP RATINGS EXPLAINED
IP RATINGS EXPLAINEDDIN VDE 0470 PART 1 /EN 60529 / IEC 529
Detailed description of each index number in the standard.
 UL94 FLAMMABILITY TESTS EXPLAINED
UL94 FLAMMABILITY TESTS EXPLAINEDTest for plastic materials according to UL94- 5VA, 5VB, V-0, V-1, V-2 and HB.
 DOCUMENT VIEWERS & PLUG-INS
DOCUMENT VIEWERS & PLUG-INSDownload the latest viewers and plug-ins to read all the documents/drawings on this website.

-
About OKW
OKW ENCLOSURES LTDOKW Enclosures Ltd is the UK subsidiary of OKW Gehäusesysteme GmbH of Germany. Our company was founded in 1987 and is based in Fareham in Hampshire.
 70 YEARS OF INNOVATION
70 YEARS OF INNOVATIONOKW Gehäusesysteme is a German company with headquarters in Buchen/Odenwald. Learn more about our company, its history and corporate culture, and our worldwide network.
 PRODUCT DESIGN AWARDS
PRODUCT DESIGN AWARDSWe have received international awards for innovation and the design excellence of our products.
 ENVIRONMENTAL POLICIES
ENVIRONMENTAL POLICIESOur engineers and designers attach particular importance to the use of materials and substances which do not pollute our living environment.
 OKW PRIVACY POLICY - GDPR (EU) 2016/679
OKW PRIVACY POLICY - GDPR (EU) 2016/679OKW's Privacy Policy provides you with information on how we collect and process your personal data when you interact with us via our websites, through emails etc.
 OKW COOKIE POLICY
OKW COOKIE POLICYLearn more about how we use cookies in order to provide you with the best online service and website functionality.

-
Contact
CONTACT OKW ENCLOSURES LTDFull contact details including opening hours and meet our team. Plus how to make an enquiry or request a sample and/or quotation.
 GENERAL ENQUIRIES FORM
GENERAL ENQUIRIES FORMUse our contact form for general enquiries and requests for information, and to upload your documents and pictures.
 HOW TO FIND US
HOW TO FIND USTravel information if you are visiting our sales and production facilities in Fareham, Hampshire, United Kingdom.
 Worldwide Sales Network
Worldwide Sales NetworkHere you can find your local OKW contact.
We have subsidiaries in 8 countries and long-standing sales partners worldwide who are ready to help you.